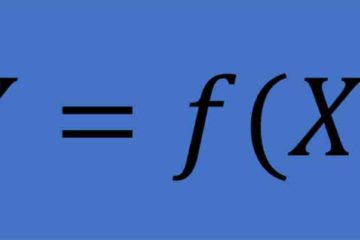Lean Terms
X (Variable)
“X” is often used as the notation for a random variable or independent variable, as in the basic transfer function, Y=f(x). In that notation, y would be the dependent variable. In practical use, X is the variable that you are experimenting on to see what impact it has on the Read more…