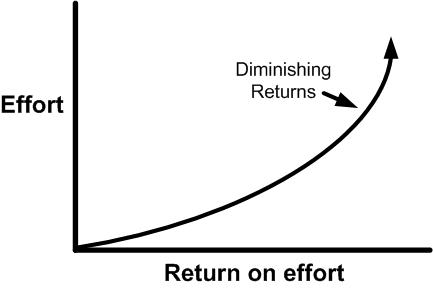
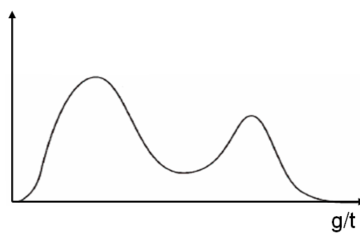
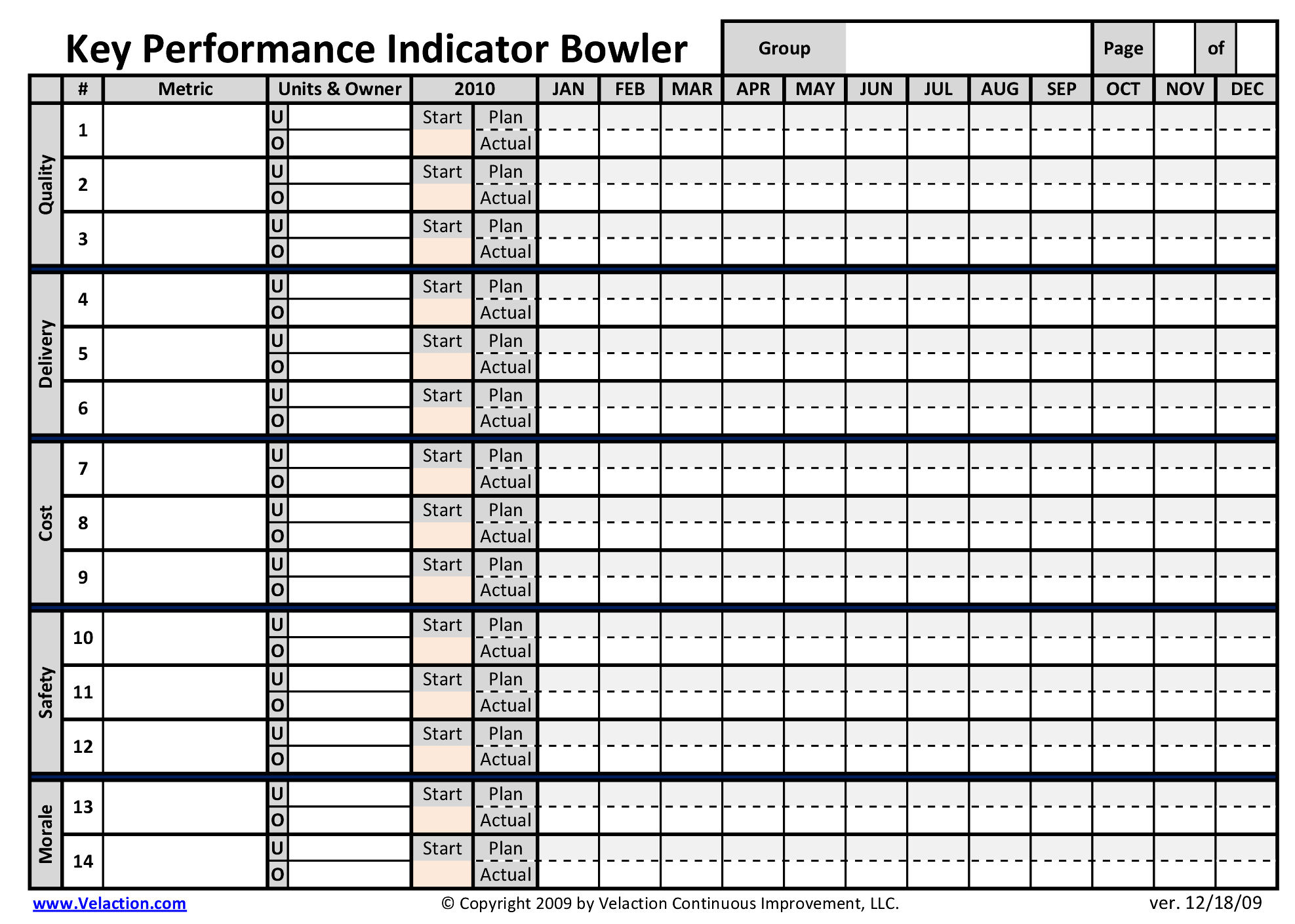
Our extensive Lean Glossary contains several hundred terms and is growing all the time. These Lean definitions go way beyond the ordinary, though. Most are extremely long and packed with content about how the term affects you in building a continuous improvement culture.
These listings are part of our Continuous Improvement Companion, and are critical to developing a Lean Business System.