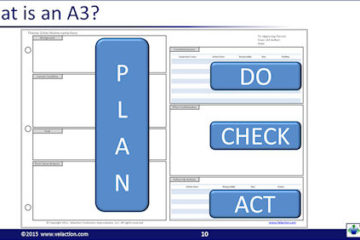
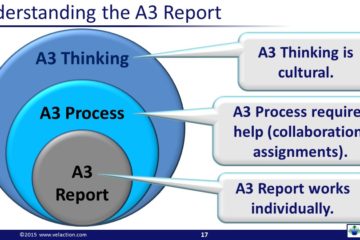
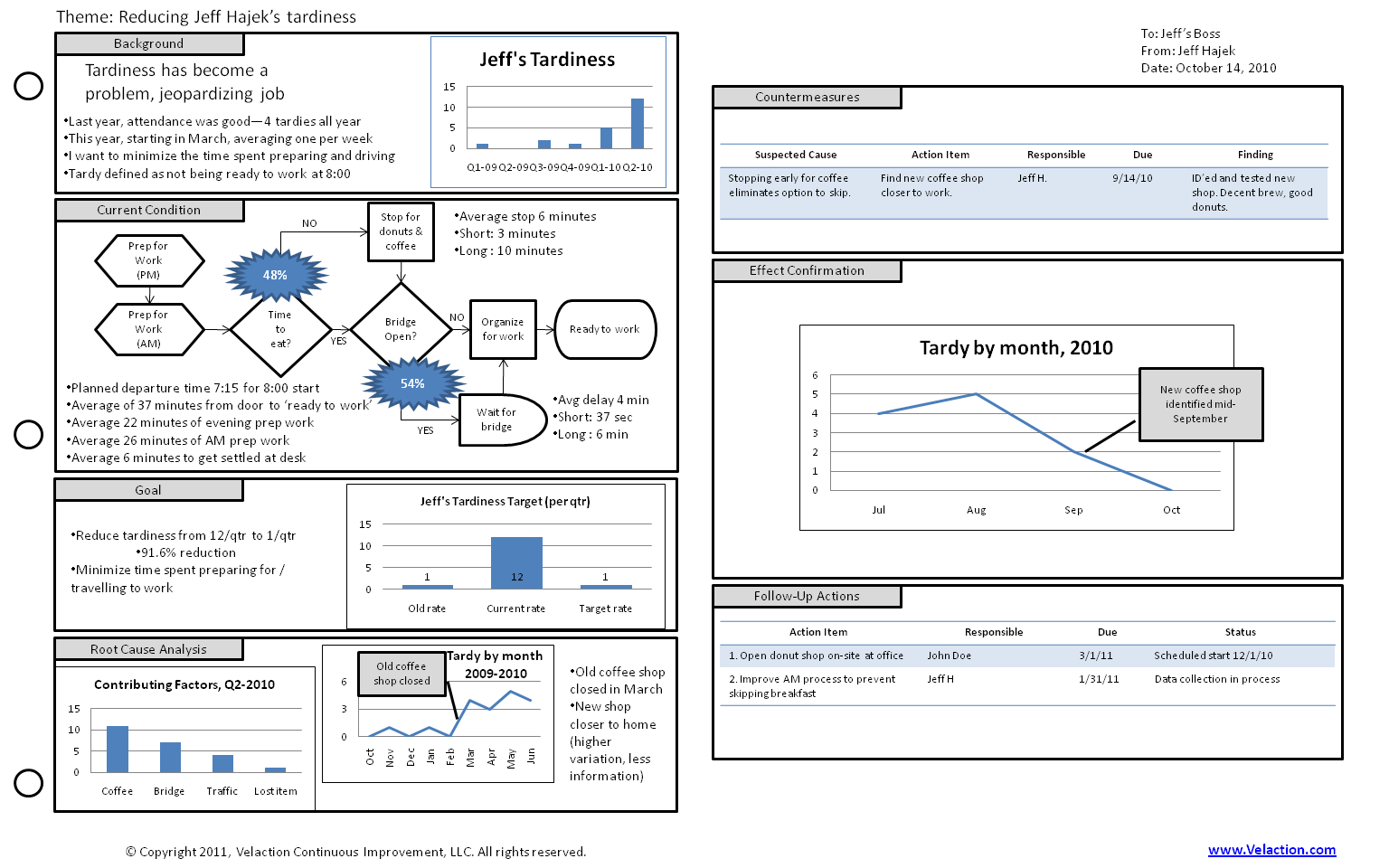
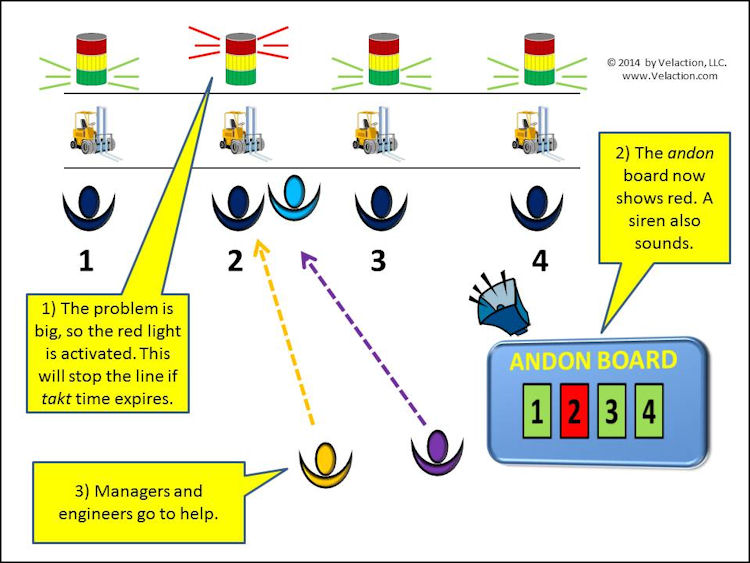
Our directory of Lean Terms contains one of the most extensive listing you will find anywhere on the internet. In addition to being exhaustive in scope, there is also a great deal of depth to our Lean terms.
Most have a lengthy write-up. Many may also have a download or MP3 available as well.